Tutorial sul controller del lettore top-down per Unity
Molte persone hanno familiarità con generi di giochi come FPS (sparatutto in prima persona) e RTS (strategia in tempo reale), ma ci sono anche molti giochi che non rientrano in una sola categoria specifica. Uno di questi giochi è lo sparatutto dall'alto.
Top-Down Shooter è un gioco in cui il giocatore è controllato da una prospettiva dall'alto.
Esempi di sparatutto dall'alto verso il basso sono Hotline Miami, Hotline Miami 2, Original Grand Theft Auto, ecc.

Per creare un controller di carattere top-down in Unity, segui i passaggi seguenti.
Passaggio 1: crea gli script
Per questo tutorial, avremo bisogno di un solo script.
- Crea un nuovo script, chiamalo SC_TopDownController, rimuovi tutto da esso e incolla il codice seguente al suo interno:
SC_TopDownController.cs
using UnityEngine;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Rigidbody))]
[RequireComponent(typeof(CapsuleCollider))]
public class SC_TopDownController : MonoBehaviour
{
//Player Camera variables
public enum CameraDirection { x, z }
public CameraDirection cameraDirection = CameraDirection.x;
public float cameraHeight = 20f;
public float cameraDistance = 7f;
public Camera playerCamera;
public GameObject targetIndicatorPrefab;
//Player Controller variables
public float speed = 5.0f;
public float gravity = 14.0f;
public float maxVelocityChange = 10.0f;
public bool canJump = true;
public float jumpHeight = 2.0f;
//Private variables
bool grounded = false;
Rigidbody r;
GameObject targetObject;
//Mouse cursor Camera offset effect
Vector2 playerPosOnScreen;
Vector2 cursorPosition;
Vector2 offsetVector;
//Plane that represents imaginary floor that will be used to calculate Aim target position
Plane surfacePlane = new Plane();
void Awake()
{
r = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
r.freezeRotation = true;
r.useGravity = false;
//Instantiate aim target prefab
if (targetIndicatorPrefab)
{
targetObject = Instantiate(targetIndicatorPrefab, Vector3.zero, Quaternion.identity) as GameObject;
}
//Hide the cursor
Cursor.visible = false;
}
void FixedUpdate()
{
//Setup camera offset
Vector3 cameraOffset = Vector3.zero;
if (cameraDirection == CameraDirection.x)
{
cameraOffset = new Vector3(cameraDistance, cameraHeight, 0);
}
else if (cameraDirection == CameraDirection.z)
{
cameraOffset = new Vector3(0, cameraHeight, cameraDistance);
}
if (grounded)
{
Vector3 targetVelocity = Vector3.zero;
// Calculate how fast we should be moving
if (cameraDirection == CameraDirection.x)
{
targetVelocity = new Vector3(Input.GetAxis("Vertical") * (cameraDistance >= 0 ? -1 : 1), 0, Input.GetAxis("Horizontal") * (cameraDistance >= 0 ? 1 : -1));
}
else if (cameraDirection == CameraDirection.z)
{
targetVelocity = new Vector3(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal") * (cameraDistance >= 0 ? -1 : 1), 0, Input.GetAxis("Vertical") * (cameraDistance >= 0 ? -1 : 1));
}
targetVelocity *= speed;
// Apply a force that attempts to reach our target velocity
Vector3 velocity = r.velocity;
Vector3 velocityChange = (targetVelocity - velocity);
velocityChange.x = Mathf.Clamp(velocityChange.x, -maxVelocityChange, maxVelocityChange);
velocityChange.z = Mathf.Clamp(velocityChange.z, -maxVelocityChange, maxVelocityChange);
velocityChange.y = 0;
r.AddForce(velocityChange, ForceMode.VelocityChange);
// Jump
if (canJump && Input.GetButton("Jump"))
{
r.velocity = new Vector3(velocity.x, CalculateJumpVerticalSpeed(), velocity.z);
}
}
// We apply gravity manually for more tuning control
r.AddForce(new Vector3(0, -gravity * r.mass, 0));
grounded = false;
//Mouse cursor offset effect
playerPosOnScreen = playerCamera.WorldToViewportPoint(transform.position);
cursorPosition = playerCamera.ScreenToViewportPoint(Input.mousePosition);
offsetVector = cursorPosition - playerPosOnScreen;
//Camera follow
playerCamera.transform.position = Vector3.Lerp(playerCamera.transform.position, transform.position + cameraOffset, Time.deltaTime * 7.4f);
playerCamera.transform.LookAt(transform.position + new Vector3(-offsetVector.y * 2, 0, offsetVector.x * 2));
//Aim target position and rotation
targetObject.transform.position = GetAimTargetPos();
targetObject.transform.LookAt(new Vector3(transform.position.x, targetObject.transform.position.y, transform.position.z));
//Player rotation
transform.LookAt(new Vector3(targetObject.transform.position.x, transform.position.y, targetObject.transform.position.z));
}
Vector3 GetAimTargetPos()
{
//Update surface plane
surfacePlane.SetNormalAndPosition(Vector3.up, transform.position);
//Create a ray from the Mouse click position
Ray ray = playerCamera.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition);
//Initialise the enter variable
float enter = 0.0f;
if (surfacePlane.Raycast(ray, out enter))
{
//Get the point that is clicked
Vector3 hitPoint = ray.GetPoint(enter);
//Move your cube GameObject to the point where you clicked
return hitPoint;
}
//No raycast hit, hide the aim target by moving it far away
return new Vector3(-5000, -5000, -5000);
}
void OnCollisionStay()
{
grounded = true;
}
float CalculateJumpVerticalSpeed()
{
// From the jump height and gravity we deduce the upwards speed
// for the character to reach at the apex.
return Mathf.Sqrt(2 * jumpHeight * gravity);
}
}![]()
Passaggio 2: crea lo shader
Questo tutorial richiede anche uno shader personalizzato, necessario per far sì che il target Aim si sovrapponga al resto degli oggetti (sempre in primo piano).
- Fare clic con il tasto destro sulla vista Progetto -> Crea -> Shader -> Shader di superficie standard
- Assegna un nome allo shader "Cursor"

- Apri lo shader, rimuovi tutto al suo interno quindi incolla il codice seguente:
Cursore.shader
Shader "Custom/FX/Cursor" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Base", 2D) = "white" {}
}
CGINCLUDE
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
half4 _MainTex_ST;
struct v2f {
half4 pos : SV_POSITION;
half2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
v2f vert(appdata_full v) {
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos (v.vertex);
o.uv.xy = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.texcoord, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag( v2f i ) : COLOR {
return tex2D (_MainTex, i.uv.xy);
}
ENDCG
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType" = "Transparent" "Queue" = "Transparent+100"}
Cull Off
Lighting Off
ZWrite Off
ZTest Always
Fog { Mode Off }
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass {
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#pragma fragmentoption ARB_precision_hint_fastest
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack Off
}![]()
Passaggio 3: imposta il controller del personaggio dall'alto verso il basso
Impostiamo un controller di carattere top-down:
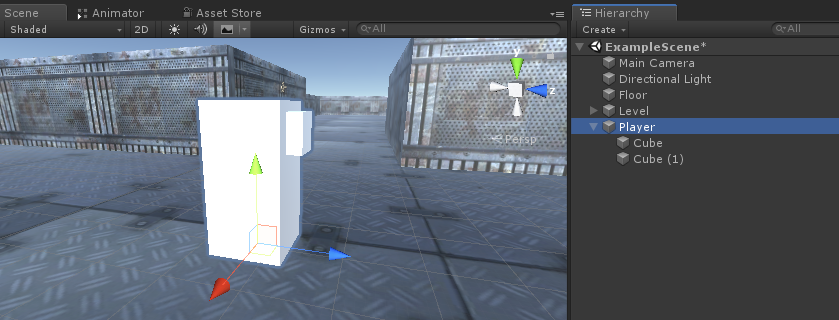
- Crea un nuovo GameObject e chiamalo "Player"
- Crea un nuovo cubo e ridimensionalo (nel mio caso la scala è (1, 2, 1))
- Crea un secondo cubo, ridimensionalo molto più piccolo e spostalo in un'area superiore (questo serve semplicemente per sapere in quale direzione sta guardando il giocatore)
- Sposta entrambi i cubi all'interno dell'oggetto "Player" e rimuovi i relativi componenti BoxCollider
Ora, prima di andare oltre, creiamo il prefabbricato target Aim:
- Crea un nuovo GameObject e chiamalo "AimTarget"
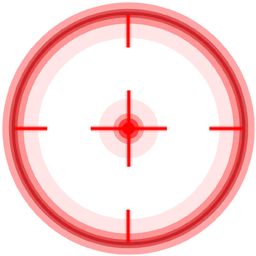
- Crea un nuovo Quad (GameObject -> Oggetto 3D -> Quad) e spostalo all'interno dell'Oggetto "AimTarget"
- Assegna la Texture sottostante a un Quad e modifica il Material Shader in 'Custom/FX/Cursor'

- Salva l'"AimTarget" in Prefab e rimuovilo dalla scena
![]()
Torniamo all'istanza del Player:
- Collega lo script SC_TopDownController all'oggetto "Player" (noterai che ha aggiunto alcuni componenti aggiuntivi come Rigidbody e CapsuleCollider)
- Ridimensiona CapsuleCollider finché non corrisponde al modello del giocatore (nel mio caso l'altezza è impostata su 2 e il centro è impostato su (0, 1, 0)

- E infine, assegna le variabili "Player Camera" e "Target Indicator Prefab" in SC_TopDownController

L'istanza Player è ora pronta, testiamola:
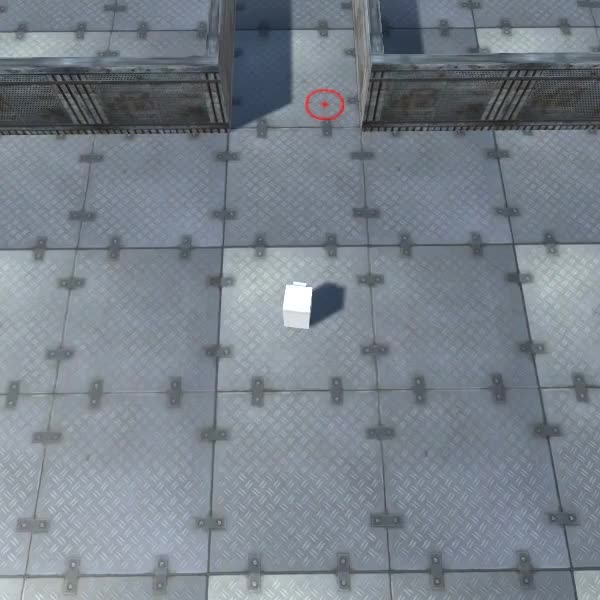

Tutto funziona come previsto.